
One of the common symptoms that patients come to a medical facility with is hip pain. The causes, treatment and possible diseases that cause such a manifestation cannot be identified without qualified medical assistance. Discomfort in any part of the musculoskeletal system can indicate the development of serious pathologies, so hip joint dysfunction should not be ignored.
Anatomy of the hip joint area
The hip joint plays an important role in motor activity. It is one of the largest human joints that can withstand high loads in the standing position as well as when walking upright.
Bones that form a joint
The hip joint is formed by the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the innominate pelvic bone - the most powerful and large parts of the human skeleton. The minimum number of anatomical elements of the joint ensures its strength and reliability, the ability to withstand body weight during movement. Most pathologies of the hip joint begin with damage to the acetabulum, the immovable part of the joint. It has the shape of a bowl, the center of which is directed upwards at a slight angle, which ensures an even distribution of the load between the pelvic bones.
The glenoid cavity is a strong and solid formation that consists of 3 types of pelvic bones:
- ileal
- ischial
- pubis
The most vulnerable area of the joint cavity is in children whose bone tissue is not strong enough. Due to the presence of a small bone edge on the edge of the socket, the head of the femur is completely immersed in the "bowl", which provides a strong support for the limb. The movable part of the joint is the femur (head, neck, greater and lesser trochanters). The shape ofthe head corresponds to the cavity of the joint cavity. It is covered with cartilaginous tissue, which ensures a perfect arrangement of the articular elements and their smooth sliding. In the center of the head, there is a strong ligament that connects the bone to the acetabulum, providing additional traction and support.
The neck protrudes from the head of the femur at an obtuse angle, which ensures mobility of the joint and an even distribution of the load between the limbs. The trochanters are bony projections to which muscle tendons are attached.
Fabrics and constructions
The normal functioning of the joint is ensured by different structures, each of which performs the respective functions.
Blood supply, workability and reduced sensitivity of the joint are provided by:
- Ligaments and tendons surround the joint on all sides, covering and protecting the femur and its neck, as well as the socket itself.
- Cartilage covers the head of the femur and part of the acetabulum.
- Subcartilaginous areas are bony tissue consisting of cells and connective extracellular substance.
- The joint membrane or capsule is a source of a special secretion - synovial fluid to lubricate the parts of the joint.
- The acetabular labrum connects the edge of the acetabulum and the transverse ligament.
The hip joint is supplied with nutrients through a fairly isolated network of vessels and arteries. The blood supply to the internal parts of the joint is provided by the acetabular branch of the obturator artery, and the capsules, ligaments and surrounding muscles are supplied by the deep femoral and gluteal arteries.
Anatomical formations located next to the hip joint
Often the cause of pain in the hip joint is damage to the anatomical structures located next to it. These items include:
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue - the outer covering of the body
- The muscles of the thigh, pelvis, lower back and buttocks ensure the mobility of the joint and further strengthen it from the outside
- Extra-articular ligaments - perform a strengthening function, located around the joint capsule
- Periarticular bursae are bundles of connective tissue that prevent friction between soft and hard tissues
Risk factors
Inflammatory processes in the pelvic area occur due to mechanical damage or damage to certain types of bacteria. In this case, both the elements of the joint and the anatomical formations surrounding them can be exposed to pathological effects.
As a rule, one or more structures become inflamed:
- Leather
- muscles
- ligaments (extra-articular, femoral heads)
- periarticular bursae
- TBS capsule
- cartilage
- acetabular labrum
- subcartilaginous areas
Pain in the hip joint is often caused by harmful microorganisms that provoke the development of infectious arthritis. Other causes are also common:
- disorders of the immune system
- joint injuries due to excessive physical activity
- old age
- metabolic disorders
- other diseases
Characteristics of pain
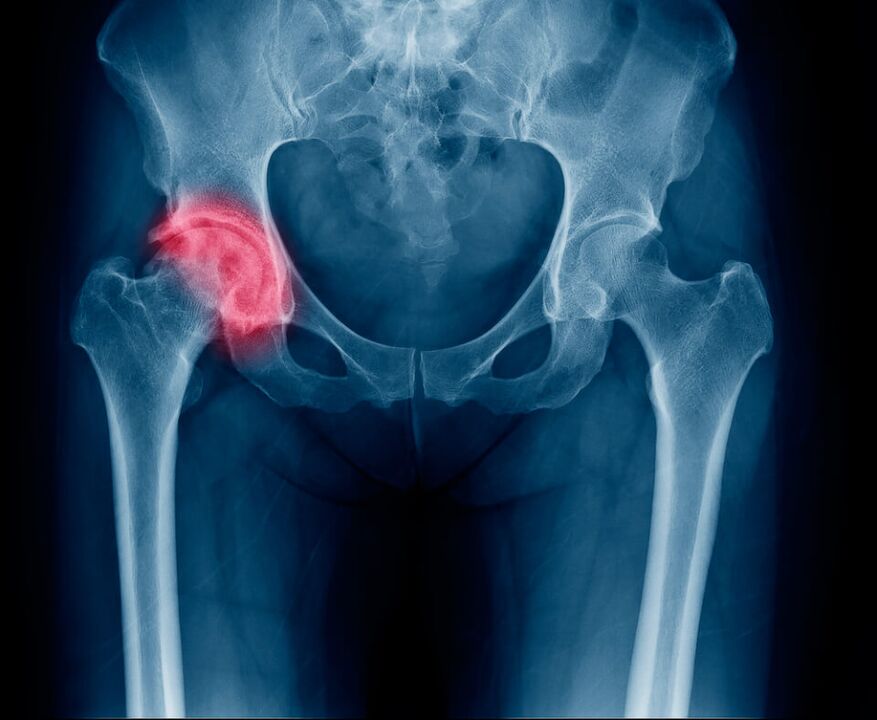
In the diagnosis of hip pain, additional symptoms play an important role, which can indicate the root cause of the problem.
Pain in the hip joint and radiates to the leg
If the pain from the inflamed joint radiates to the groin, knees or buttocks, the problem is most likely caused by damage to the nerve innervating the leg area due to one of the following reasons:
- joint tumor
- infectious arthritis - occurs due to damage from a pathogen
- fracture of the femur (in the head or neck area)
- Pathology of Legg-Calvé-Perthes - necrosis of the cartilage tissue of the head of the femur
- juvenile epiphysiolysis - disruption of the structure of the head of the joint and its inflammation
Pain in the hip joint radiating to the leg can signal pathologies of the cartilage tissue and periarticular structures, lack of lubrication of the joint and damage to the synovial membrane. Painful symptoms can appear suddenly or gradually increase.
Pain when walking
Pain in the hip joint can occur while walking if the acetabulum comes into contact with the cartilage tissue of the femoral head, leading to an inflammatory process. The cause of this phenomenon can be mechanical damage, inflammation of anatomical formations located next to the joint.
Based on the intensity of pain in the hip joint when walking, you can identify the main cause of the problem:
- discomfort that appears at the beginning of walking gradually decreases - a sign of inflammation of the periarticular bursa
- discomfort that gradually increases from the moment you start walking - inflammation of the articular surfaces of the hip joint
- long-lasting pain of high intensity, accompanied by impaired functionality of the joint - occurs with dislocations and fractures
- the pain appears closer to the night - a consequence of deformation of the cartilage of the head of the femur and (or) the acetabulum, which rub against each other and become inflamed
- pain of moderate intensity is a sign of minor injuries and bruises
Pain on abduction of the leg
Pain in abduction of the leg is caused by inflammation of the tissues and structures that provide movement: muscles, periarticular bursae, tendons. Similar symptoms often result from myositis (inflammation of muscle tissue), bursitis (inflammation of the periarticular bursa), and tendinitis (inflammation of tendons).
reasons
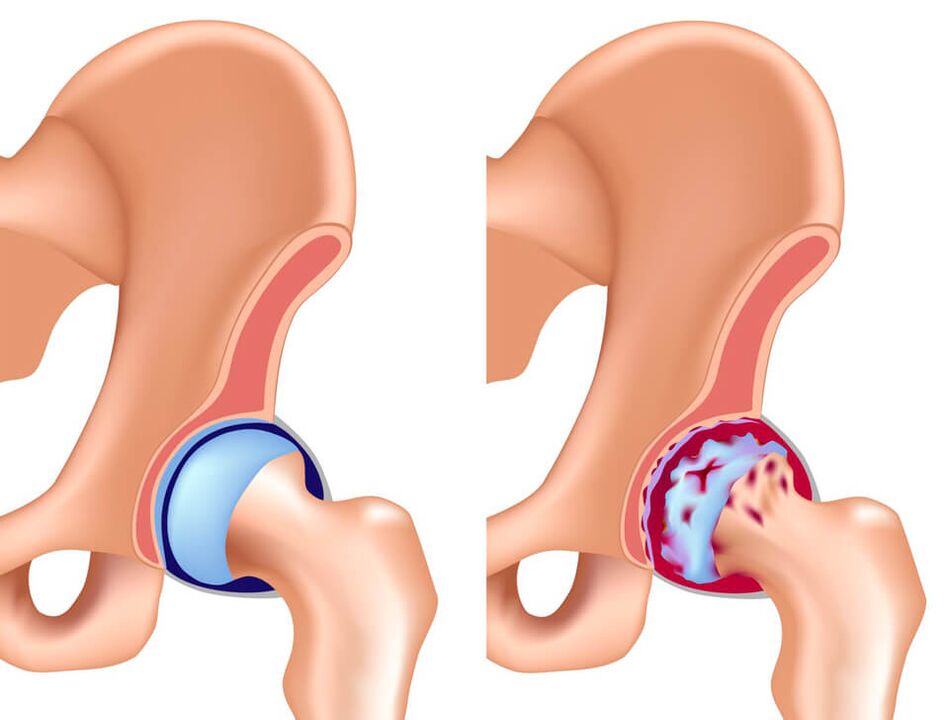
In most cases, pelvic pain is caused by a patient who has one of the following problems:
- arthritis
- coxarthrosis
- bursitis of the trochanteric bursa
- tendinitis
- infectious pathologies
- hereditary diseases
- formation of tumors in the pelvis
Without prompt treatment, any of these causes can lead to severe complications, including loss of joint mobility.
Arthritis
Arthritis (coxitis) is a disease of joint tissue caused by disorders of the immune system or damage by pathogens: viruses and bacteria.
Symptoms of arthritis:
- rise in temperature
- pain and swelling in the joint area
- motor impairment
The disease occurs in acute, subacute and chronic form.
Coxarthrosis
Another name for coxarthrosis is osteoarthritis of the hip joint. This pathology is caused by metabolic disorders in cartilaginous tissues, which leads to their death. The cause of this phenomenon can be injury, impaired blood supply, excessive physical activity, age over 45 and heredity. The main symptom of coxarthrosis is pain in the lower back, groin and buttocks, which gradually increases during physical activity and leads to lameness. Discomfort decreases during periods of inactivity.
Bursitis of the trochanteric bursa
The presence of an inflammatory process in the bursa (trochanteric bursa) is characterized by the appearance of intense pain in the joint area. Athletes and the elderly are susceptible to the disease. The main symptom of bursitis of the trochanteric bursa is pain in the area of the greater trochanter, which increases when you try to lean on the affected leg.
Tendinitis
Inflammation of tendons is called tendinitis. It is a disease that occurs in an acute or chronic form and leads to degenerative changes in the tissues. Often the pathology occurs in athletes who do not follow the technique of running, as well as after a heavy load on the thigh muscles.
Tendinitis is usually a complication of another disease:
- thyroid pathology
- metabolic disorders
- arthritis
- arthrosis
- inflammatory process of systemic or infectious origin
- hip dysplasia
Tendinitis causes the patient discomfort during movement, pain, changes in gait and clicking when walking in the area of the joint.
Infections
Some infectious diseases cause inflammation of the joint tissues, as well as the nearby anatomical structures, which leads to severe pain in the hip joint. Most often, the following pathologies have similar symptoms:
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is a violation of blood supply to the groin area, which leads to tissue death. The pain associated with this disease is sharp and intense. The problem is more common in men.
- Purulent arthritis is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment. If you don't seek medical help promptly, sepsis can occur. Accompanying symptoms are general intoxication, pain and swelling in the area of the affected joint, impaired motor activity.
- Tuberculous arthritis is common in children and is characterized by slow progression. Associated symptoms are increased fatigue, decreased motor activity and muscle atrophy. Pain of varying intensity increases when a purulent abscess appears.
Infectious pathologies of the hip joint lead to severe complications and therefore require immediate treatment.
Hereditary diseases
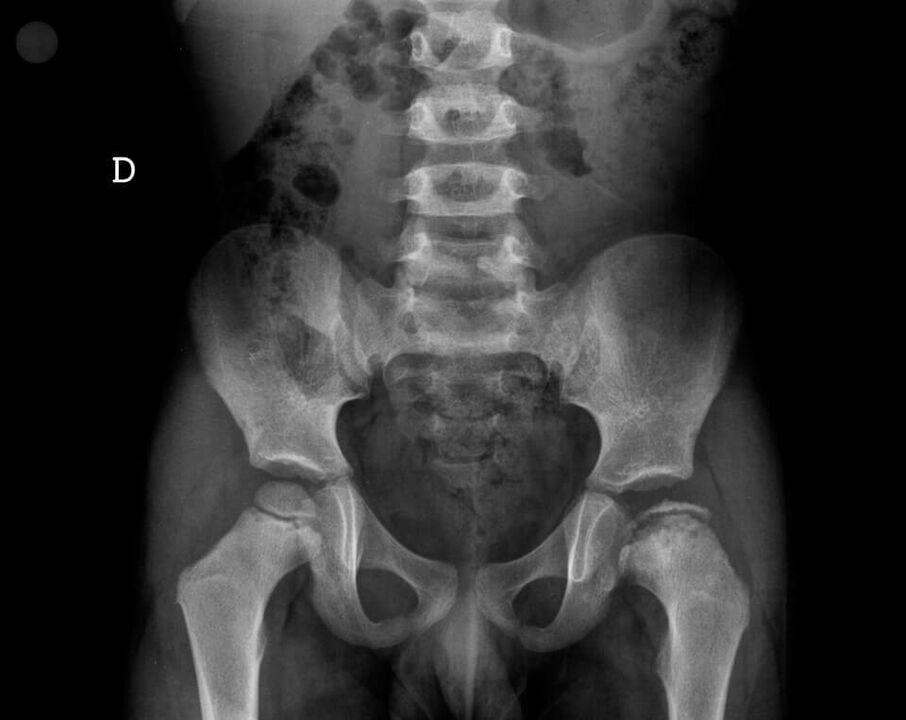
Hereditary pathologies of the hip joint usually appear between the ages of 1 and 10 years and are characterized by pathological changes in the tissue of the glenoid cavity and/or the femoral head. The most common hereditary disease affecting the hip joint is Legg-Calvé-Perthes syndrome, which is characterized by pain and gait disturbance due to the death of cartilage tissue in the joint.
Bone and soft tissue tumors
Benign or malignant bone and soft tissue growths in the hip joint can cause pain when walking or at rest. The tumor can appear in bone tissue (osteomyelitis), cartilage tissue (chondroblastoma, chondroma), osteochondral tissue (osteochondroma). As a rule, neoplasms cause discomfort and are felt during palpation. Benign tumors are treated surgically, some of them can transform into cancerous tumors.
Soft tissue tumors of the thigh:
- lipoma
- rhabdomyoma
- fibroma
- hemangioma
- neuroma
The oncologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of tumors in the hips and pelvis.
What to do
With severe pathologies of the hip joint, a person experiences severe pain. Pelvic discomfort is a reason to visit a medical facility for examination and treatment.
Particular attention should be paid to the intensity of the pain:
- Lungs- occur with bruises after injury. Cold should be applied to the affected area to reduce swelling. To reduce pain, it is recommended to take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It is recommended to consult a doctor.
- Moderate- usually occur in diseases of the hip joint, accompanied by difficulties in motor activity and increased body temperature. Discomfort increases during physical activity. Consultation with a rheumatologist is necessary.
- Strong- occur due to dislocations and fractures. Accompanied by limitation or impossibility of physical activity. In case of severe pain in the hip joint caused by an injury, you should contact an ambulance.
There are many folk recipes that are used for hip pain. It is important to remember that all of them are suitable for symptomatic treatment and pain reduction, but will not help to eliminate the cause of the problem. Effective treatment is carried out exclusively under the supervision of a qualified doctor.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have hip pain, you should contact your family or general practitioner who will refer you to a specialist. Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are treated:
- traumatologist— pain in the hip joint due to physical activity, sprains, falls and other injuries
- rheumatologist- sudden onset of joint pain for no apparent reason
You may also need to consult with other doctors: a surgeon, an oncologist, an infectious disease specialist, etc.
Diagnosis
The first important stage in the diagnosis of pain in the hip joint is an external examination, which necessarily includes taking an anamnesis and palpation. Depending on the severity of the disease and the patient's complaints, laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- radiography- the use of X-rays to examine a certain area of the body
- CT and MRI- modern accurate diagnostic methods that allow you to get highly informative images of the joint and the area around it
- microbiological examination of a sample of biological materialallow to detect the presence of pathogenic microorganisms: viruses and bacteria
- immunological blood test- allows you to identify immune disorders, determine the presence of certain autoantibodies
- arthroscopy (endoscopic examination)— examination using a probe, the possibility of taking a sample of joint tissue for further examination
- laboratory examination of effusion- taking a sample of intra-articular fluid during a puncture and identifying the causative agent of an infectious disease in it, checking for sterility
Using several diagnostic methods in combination allows us to identify the cause of hip pain with high accuracy.
Treatment

Treatment of hip pain should be prescribed by a doctor based on the examination and diagnosis. As a rule, drug therapy or surgical intervention is prescribed.
medicines
Treatment of pain in the hip joint should be comprehensive, aimed at eliminating the symptoms and most importantly - eliminating the cause of the problem. For this purpose, drug therapy is used, which includes the use of:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs- help reduce pain, relieve swelling
- means to improve microcirculation- support the restoration of blood circulation and nutrition of joint tissues
- chondroprotectors- promotes the recovery of cartilage tissue
- muscle relaxants- reduction of pain, improvement of blood flow in the damaged area
- hormonal drugs- to relieve pain and suppress inflammation
In the treatment of pain in the hip joint, physiological procedures are highly effective: massage, acupuncture, cryo- and laser therapy. Special therapeutic exercises and manual therapy are also used.
Surgically
Surgical intervention is indicated in advanced cases when conservative treatment does not help the patient. This involves partial or total replacement of the diseased joint with a prosthesis.
Prevention
Reducing the load on the legs will slow down the pathological processes inside the joint, so obese people are recommended to start losing weight.
Preventive measures will help reduce hip pain:
- regular walking
- physiotherapy
- a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, E
Timely consultation with a doctor in the first stages of the disease increases the effectiveness of treatment and also reduces the risk of complications and serious consequences for the body.

















































